Data Governance: The Backbone of Digital Transformation

According to Yahoo Finance, the data governance market is predicted to reach $22.5 billion by 2034, increasing at a 18.5% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). As this market continues to grow, many enterprises struggle to leverage data assets and insights in an effective and efficient manner. Whether the goal is to enhance operational processes or gain a better understanding of clients and customers, a good data strategy establishes governance, ownership, and desired outcomes for all data. With increased focus on digital transformation, the shift to agile data governance emphasizes the importance of data accuracy and accessibility, standards and regulations, security and storage, as well user demands and business intelligence. Digital transformation creates more troves of insightful data and analytics, making a strong data governance program critical to organizational success.
What is data governance and its pillars?
To explore the intricacies of data governance, it is important to understand its definition and guiding principles that make it impactful in support of digital transformation. Microsoft states, “Data governance is the system of internal policies that organizations use to manage, access, and secure enterprise data… The goal of the system is to help people efficiently and securely use the vast amounts of data generated by today’s enterprises.” Although systems vary with each organization, common features include internal processes, defined roles, key metrics, and compliance standards. With the increased market pressure to undergo digital transformation, it is pertinent for organizations to leverage existing and newly created strands of data to remain competitive and agile in the evolving landscape of tech empowerment.
As data governance represents a large conceptual approach to effectively manage and utilize data, it can be beneficial to sift through its key components and principles. Industry accepted frameworks such as DAMA-DMBOK are important for standardization and clearly defined principles of what constitutes data governance. For example, the functional areas of data governance according to DAMA-DMBOK, which account for its primary elements, includes:
- Data Architecture
- Data Development
- Database Operations
- Data Security
- Reference & Master Data
- Data Warehousing & Business Intelligence
- Document & Content Management
- Metadata
- Data Quality
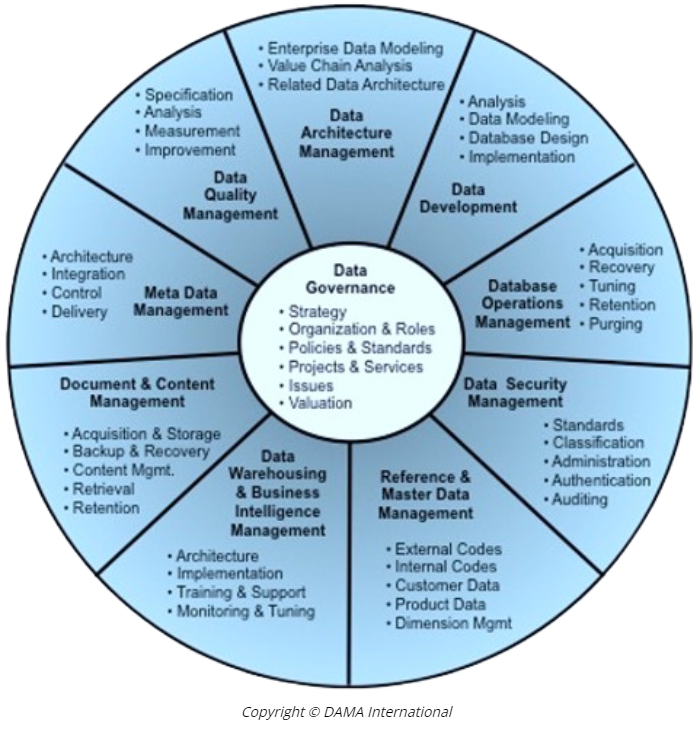
Data Governance serves as the central hub connecting each of these functional areas and ensures accountability across the organization. For data governance to truly work, it must be ingrained throughout all divisions and departments, systematically connected into enterprise-wide operational and technical processes. This means the responsibility of managing a data governance program rests on the shoulders of the collective instead of a singular resource. There are many key roles to be played in the implementation and sustainability of this program.
Next, let’s look at the pillars of data governance and how each principle helps maintain the integrity and usefulness of data lifecycles. Through this framework, organizations can rest assured that comprehensive coverage of data management, utilization and disposal is appropriately addressed. These essential pillars include:
- Quality – Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. High-quality data is essential for making informed decisions and maintaining trust in the data. This involves metrics and methods for error identification and correction, balanced representation, and continuous validation processes during to uphold data integrity and usefulness.
- Administration (Data Stewardship) – Assigning responsibility for data management and ensuring that data stewards are accountable for maintaining data integrity, quality, and privacy. Data stewards enforce data governance policies and procedure.
- Security – Focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security threats. This includes implementing encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems to safeguard data.
- Standards / Ethics – Practices that comply with relevant laws, regulations, and standards. This includes adhering to industry-specific regulations, data protection laws and internal policies. This also includes integrating ethical considerations into data governance to certify data is used responsibly and fairly.
- Data Management – Encompasses the overall management of data as an asset. This includes data architecture, data modeling, metadata management, and data lifecycle management. Effective data management ensures that data is organized, accessible, and usable across the organization.
Through understanding these standardized definitions and principles, data governance becomes more manageable and achievable. It provides each key stakeholder in the data governance program with a clearly defined role on both the individual and organizational level. This not only provides key insights and fundamental knowledge, but also establishes a proven framework and roadmap for implementing and maintaining a comprehensive data governance system. With this system in place, organizations can feel empowered gain the most out of their enterprise data.
What are the benefits & challenges of data governance?
Before establishing a full-scale data governance program, organizations want to know if the effort will be worth it. They want assurance that investment of time and resources into building a formal data governance program will yield substantial benefits that can push the organization forward. Here’s a handful of competitive advantages to be expected when proper data governance is established:
- Single source of truth – Maintaining a single source of truth ensures that all stakeholders and decision-makers have access to the same, consistent data, which eliminates discrepancies and enhances internal coherence. This alignment enables more accurate and unified decision-making, fostering greater operational flexibility and collaboration across the organization.
- Improved data management – Effective data management, guided by a clear data code of conduct and best practices, enables organizations to address their data needs swiftly and reliably. This structured approach ensures consistency and efficiency in data handling, leading to better resource allocation and quicker responses to business challenges.
- Cost optimization – Consistent data management practices streamline operations, making processes more efficient and reducing redundancies. This operational efficiency not only facilitates smoother audits but also ensures that time and resources are allocated effectively, ultimately reducing costs and enhancing overall productivity.
- Data quality - High data quality means that data is accurate, complete, and reliable, which is critical for making informed business decisions. When data is safe to use and consistent, organizations can trust their insights and analyses, leading to better strategic planning and outcomes.
- Increased agility – A robust data governance strategy, incorporating compliance considerations at every stage, enhances an organization’s ability to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. This approach ensures correct data handling and disposal, fostering regulatory compliance and enabling the organization to respond rapidly and effectively to new opportunities and challenges.
When implemented correctly, organizations can experience each of these benefits in full and unlock newfound efficiencies and business intelligence to support digital transformation and additional strategic initiatives. While considering each of these benefits, it’s also noteworthy to anticipate challenges that may prevent data governance goals and objectives. Some common challenges include, but are not limited to:
- Continuous Data Governance – Data governance is an ongoing process rather than a one-time project. It encompasses various aspects, such as data sources, integrity, and access, all of which are constantly evolving. Improvement opportunities and priorities may shift over time. While formal projects can facilitate specific enhancements, effective data governance requires continuous improvement and delivery to strategically meet both current and future institutional needs and goals.
- Organizational adoption – The value of well-governed data is realized only when the organization actively embraces and utilizes it. Data governance thrives when every team member—executive leaders, business stakeholders, and data experts—is empowered through upskilling and collaboration to leverage organizational data effectively.
- Defined roles and teamwork – Defining clear roles and responsibilities within data governance provides clarity on who manages various aspects of the process. Titles such as chief data officer or data steward can be designated, with each organization determining the most suitable team structure based on their needs and resources. This clarity promotes better adoption and teamwork.
- Siloed data – Internal divisions in data gathering can create silos, leading to isolated data that may become duplicated or inconsistent when unified. Cleaning and preparing data is essential for successful data governance. Quality input data ensures quality output data. Addressing silos is crucial to preventing fragmentation and enhancing data consistency.
- Formalized approach / methodology – Without leveraging a proven framework or a champion advocating for a thorough methodology, gaining the broad support needed for a successful data governance initiative can be challenging. Executive-level support is vital to persuade other leaders of the necessity for improvements and collaboration which fully actualizes the benefits of data governance.
- Preparedness – There can be hesitation to start data governance initiatives, even when elements of data management are already in place. Assessing existing practices and determining next steps are critical first steps. For an institution to benefit from data governance, it is essential to begin the process and remain open to change, despite the inherent difficulties associated with change.
Challenges should be expected when embarking on any new enterprise-wide initiative, especially addressing as complex a system as data governance. The best way to overcome these challenges is head on, as avoidance and complacency makes matters worse, leaving organizations severely behind competitors who decide to take advantage of the ranging benefits provided by data governance. Even a small step forward is better than inaction when it comes to data governance and digital transformation.
Rise of AI in data governance
In the sophisticated landscape of data management and digital transformation, it’s important to analyze current and future developments, especially the impact of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). The adoption of AI capabilities into data governance programs is proving valuable in the collection, clean-up and analysis of enterprise data as well as driving real-time decision making and compliance with data policies and industry standards. Furthermore, the introduction of natural language processing and ML algorithms helps automate specific tasks and provide comprehensive independent insights with minimal need of human interference. This not only frees up valuable time and resources, but also provides an added layer of quality control to ensure all data is properly evaluated and organized. Overall, the ability to leverage AI and ML makes the process for implementing and maintaining a data governance program more efficient and effective.
When correctly integrated, AI and ML unleashes a host of benefits to empower organizational data governance. This includes locating, classifying and categorizing targeted data to enhance business intelligence and reducing data vulnerabilities and inconsistencies. Improving the process for organizing data and ensuring quality standards provides more precise understanding of the organizational innerworkings and the 1ability to forecast upcoming developments. It brings visibility into important organizational processes and performance across otherwise distant and siloed environments. This alleviates the more laborious components of data entry and analysis, allowing for data professionals to focus on larger strategic and programmatic concerns.
With such expansive capabilities, organizations must ensure AI and ML adhere to high ethical standards, liberated from biases which can malign the impact of these technologies. In 2017 alone, according to Gartner, inaccurate data costs organizations an average of $15 million annually, a figure that can be exacerbated by biased AI models which have far-reaching ripples due to its agility and pervasiveness. As such, non-biased, ethical AI systems require sensitivity analysis, fairness testing, and explainable AI to prevent discriminatory outcomes and proliferation of low-quality, incorrect data. This requires organizations establish protective safeguards around emerging technologies before blindly incorporating these tools, a necessary inconvenience that saves the integrity of enterprise data immediately and over the course of time.
Data Quality – Security and Compliance
Another major component of data quality is protection from cyber threats and compliance to industry standards. Protection from bad actors prevents intentional manipulation, corruption and theft of data critical to organizational success. As digital transformation and technical capabilities expand, there’s a twofold effect happening with the potency of cyber attacks and resources available to cyber criminals aiming to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise sensitive data. Data security must be thoroughly integrated into an effective data governance program to mitigate these risks and protect against the persistent threat of bad actors.
Robust data security requires proactive threat detection, incident response and continuous monitoring. This ensures key protections are in place to thwart the effectiveness of cyber threats before they occur and actionable steps are taken when a data breach happens. Although the best line of defense is prevention, organizations must be prepared for worst case scenarios and know how to address a compromised environment to ensure continuity of services and protection from additional damage. Adopting proven controls and countermeasures established by trusted entities such as NIST and CISA provides helpful frameworks and recommendations needed to keep organizations across all industries safe. Addressing data security with proven cybersecurity frameworks strengthens the integrity of data governance programs, and as a result, the entire organization.
Furthermore, data quality and cyber protections helps organizations remain in compliance with industry standards and regulations. For example, regulations such as FISMA for financial services and HIPAA for healthcare require organizations to adhere to stringent criteria which can be misaligned by poor data quality or exposed vulnerabilities. With proper data governance, organizations can account for the nuances of compliance to industry regulations, and rest assured that they are meeting the standards impressed upon them without being at risk for penalty or sanction. To further support compliance, continuous monitoring is needed to regularly ensure processes, practices, and environments of an organization remain compliant as standards and regulations continue to evolve. As standards change, organizations can more readily adapt when continuous monitoring is implemented into their data governance strategy and unlock the full potential digital transformation offers in making insightful business decisions.
Contact Us
Whether you establish a data governance strategy from scratch or improve upon an existing program, it is a tall task to accomplish alone. Maybe the right resources are in place to lift your data governance program off the ground and into daily practice. Maybe your internal personnel has the skillsets and availability to address comprehensive data management and protection. Even so, with the help of a trusted partner such as Seneca Resources, the process becomes significantly easier. Not only is Seneca a provider of enterprise-level consulting services and effective roadmaps to implement robust data governance programs, we also deliver the technical experts experienced in successfully building these systems, customized to the exact needs unique to your organization.
To learn more about Seneca Resources’ data governance or digital transformation capabilities, please contact us at (703) 390-9099 or info@senecahq.com.